
Blood Clots – Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment at Emirates Hospitals Group
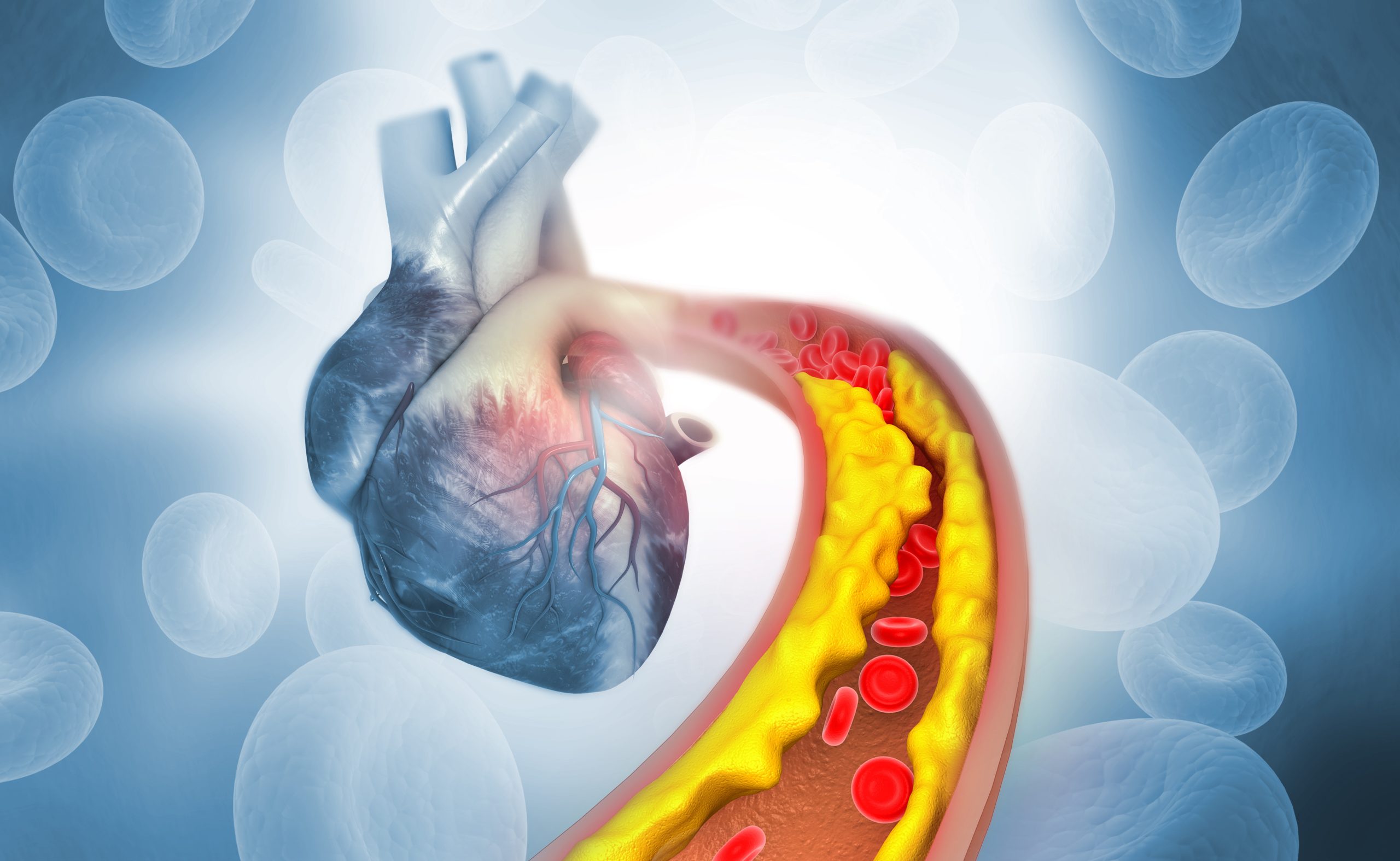
Blood clots, also known as thrombi, are gel-like masses formed by platelets and clotting factors in the blood. While essential for stopping bleeding after injury, clots can become problematic if they form within blood vessels, obstructing blood flow. These problematic clots can develop in both arteries (arterial thrombosis) and veins (venous thrombosis).
Several factors can contribute to the formation of blood clots:
- Immobility, such as prolonged sitting or bed rest, slows blood flow and increases the risk.
- Surgery, especially orthopedic procedures, can damage blood vessels and trigger clot formation.
- Certain medical conditions, including cancer, heart failure, and inflammatory diseases, can also elevate clotting risk.
- Genetic predispositions and family history of clotting disorders play a role.
- Hormonal factors, like pregnancy, birth control pills, and hormone replacement therapy, can also increase the likelihood of clots.
- Smoking damages blood vessels and thickens the blood, making clotting more likely.
- Obesity is another contributing factor.
Diagnosing blood clots involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests:
- Doppler ultrasound is commonly used to visualize blood flow and identify clots, particularly in veins.
- A D-dimer blood test measures a substance released when clots break down; elevated levels may suggest a clot but aren’t specific.
- CT or MRI scans can provide detailed images of blood vessels and clots, especially in the lungs (pulmonary embolism) or deep veins (deep vein thrombosis or DVT).
- Venography, an X-ray using contrast dye, can visualize veins but is less commonly used now.
Treatment for blood clots aims to prevent them from growing, breaking off (embolizing), and causing complications:
- Anticoagulants, or blood thinners, like warfarin or newer oral anticoagulants (NOACs), are the cornerstone of treatment, preventing further clot formation.
- Thrombolytic therapy, using drugs to dissolve clots, is used in severe cases like pulmonary embolism or large DVTs.
- Compression stockings can improve blood flow in the legs and reduce the risk of DVT.
- In some cases, a filter may be placed in the inferior vena cava (a large vein in the abdomen) to trap clots before they reach the lungs.
- Lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding smoking, are crucial for prevention and management.
Related Treatments
Request an appointment
Please complete the details and we will book you shortly.
