

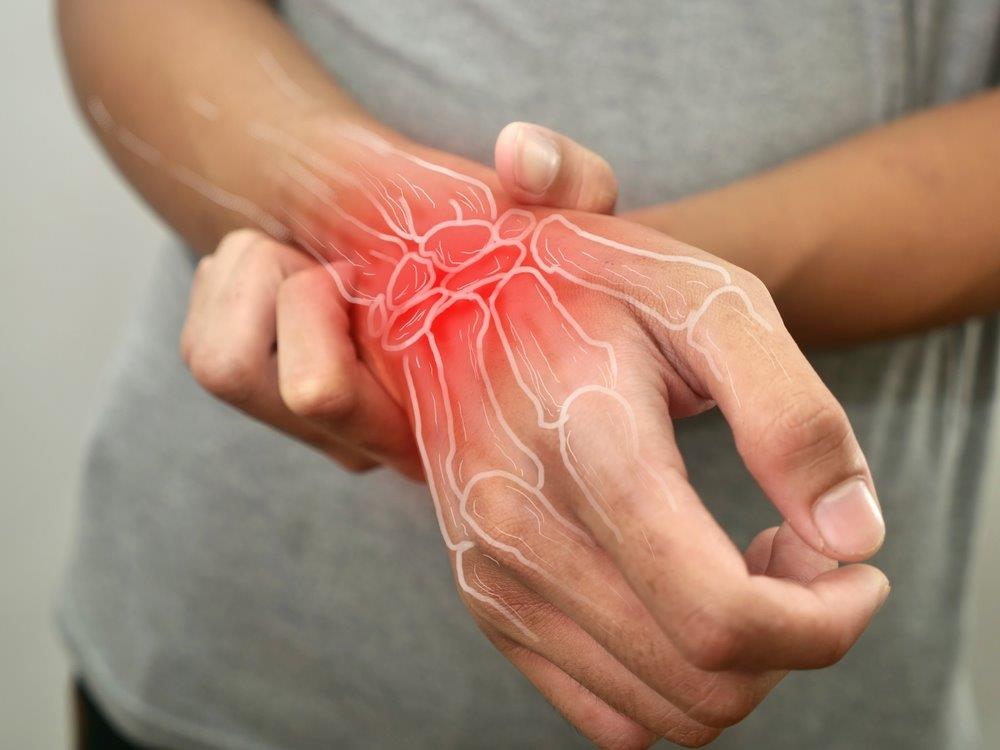
Wrist Tendonitis Treatment in Dubai at Emirates Hospitals Group. Wrist Tendonitis (Tenosynovitis) is a condition characterized by inflammation and irritation of the tendons and their protective sheaths that run through the wrist.
There are several tendons that run through the wrist, including those that control the movement of the thumb, fingers, and wrist itself.
- Symptoms & Causes
- Treatment

Symptoms of Wrist Tendonitis
Common symptoms of wrist tendonitis include pain, tenderness, and swelling in the wrist, as well as stiffness and difficulty moving the wrist and hand. The symptoms may worsen with activity or after prolonged periods of rest.
Common symptoms may include:
Pain and Tenderness in the Wrist: The affected area may be painful to the touch, and the pain may worsen with movement.
Swelling or Inflammation: The wrist may be swollen, red, or warm to the touch.
Stiffness or Restricted Movement: The wrist may feel stiff or have limited mobility, particularly when trying to move the wrist or hand.
Weakness or Loss of Grip Strength: The affected wrist may feel weak, and it may be difficult to hold objects or grip things.
A popping or Clicking Sensation: Some people may hear a popping or clicking sound when moving the wrist.
Numbness or Tingling: In some cases, wrist tendonitis can cause numbness or tingling sensations in the hand or fingers.
Common Causes of Wrist Tendonitis
Wrist tendonitis is often caused by repetitive motions or overuse, such as when playing sports, typing on a computer, or using hand tools. It can also be caused by a sudden injury or trauma, such as a fall or direct blow to the wrist.
Wrist tendonitis can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
Repetitive Strain: Activities such as typing, playing an instrument, or using hand tools, can put stress on the tendons and cause inflammation.
Overuse: Engaging in activities for extended periods of time without taking breaks can cause overuse injuries to the tendons.
Trauma: A sudden injury or trauma, such as a fall or direct blow can cause damage to the tendons and lead to inflammation.
Age-Related Wear and Tear: The tendons in the wrist can become less flexible and more prone to injury with age.
Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis or gout, can cause inflammation and lead to tendonitis.
Poor Ergonomics: Poor posture or ergonomics can put strain on the tendons in the wrist.
Genetic Factors: Some people may be more prone to developing tendonitis due to genetic factors.

Treatments for Wrist Tendonitis
The treatment for wrist tendonitis, usually involves a combination of rest, pain relief, and physical therapy. The goals of treatment are to reduce inflammation, relieve pain, and promote healing.
Here are some common treatments for wrist tendonitis:
Rest and Immobilization: Resting the affected wrist and avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms can help reduce inflammation and promote healing. A brace or splint may be recommended as well.
Ice and Heat Therapy: Applying ice packs to the affected wrist can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain. After a few days, heat therapy, such as a warm compress, can help promote blood flow and healing.
Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help reduce pain and inflammation.
Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can recommend exercises and stretches to improve flexibility and strength in the affected wrist.
Corticosteroid Injections: In some cases, a corticosteroid injection may be recommended to reduce inflammation and pain.
Surgery: In severe cases where other treatments have failed, surgery may be recommended to repair or remove damaged tendons.
Frequently Asked Questions
Wrist tendonitis is an inflammation or irritation of the tendons in the wrist, leading to pain, swelling, and limited movement.
Symptoms include pain in the wrist, swelling, tenderness, stiffness, and weakness, particularly with movement or repetitive activities.
Causes include repetitive strain or overuse of the wrist, acute injuries, poor ergonomics, and underlying conditions such as arthritis.
Diagnosis involves a medical history review, physical examination, and may include imaging studies such as ultrasound or MRI.
Treatment options include rest and immobilization, medications, physical therapy, and in some cases, surgical intervention to address severe symptoms or persistent issues.
Request an appointment
Please complete the details and we will book you shortly.
Request an appointment
Please complete the details and we will book you shortly.
