

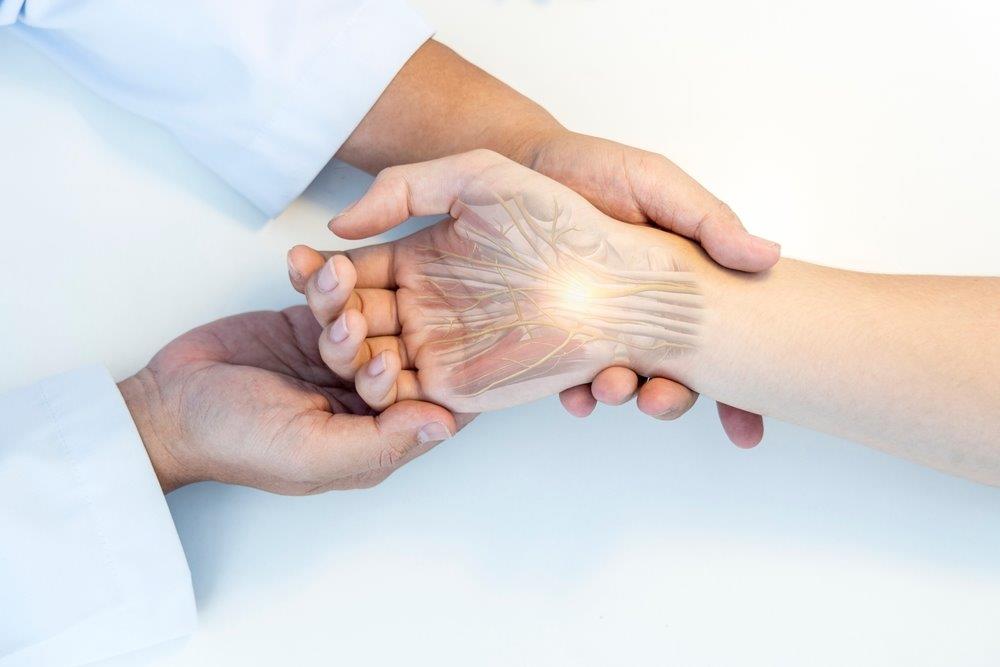
Capral Tunnel Syndrome Treatment in Dubai at Emirates Hospitals Group. Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a condition that causes pain, tingling, and numbness in the hand and arm due to compression of the median nerve as it passes through the wrist. The carpal tunnel is a narrow passageway in the wrist made up of bones and ligaments that protects the median nerve and tendons that control movement in the hand and fingers. At Emirates Hospitals Group, we are proud to have the best hand and wrist surgeons in Dubai, specializing in diagnosing and treating CTS with the latest techniques and personalized care.
- Symptoms & Causes
- Treatment

Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
The symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) usually develop gradually and may include:
- Numbness or tingling in the thumb, index, middle, and ring fingers
- Pain or discomfort in the hand, wrist, and forearm
- Weakness in the hand and difficulty gripping objects
- A sensation of swelling or tightness in the hand or wrist
- Shock-like sensations that radiate to the fingers
- Difficulty performing tasks that require fine motor skills, such as buttoning a shirt or holding a small object
- Worsening symptoms at night that may interfere with sleep
These symptoms are typically localized to the thumb, index, and middle fingers and can sometimes extend to the ring and little fingers. The symptoms may be mild at first, but they can worsen over time and may affect daily activities.
Common Cause of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Some common causes of carpal tunnel syndrome:
Repetitive Hand and Wrist Movements: Activities that require repetitive motions of the hand and wrist, such as typing, playing a musical instrument, and assembly line work, can lead to CTS.
Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions such as diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, thyroid disorders, and obesity may increase the risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome.
Pregnancy: The hormonal changes during pregnancy can cause swelling and inflammation, leading to carpal tunnel syndrome.
Wrist Injuries: Fractures or sprains of the wrist can cause swelling and inflammation, putting pressure on the median nerve.
Genetics: Some people may be more prone to carpal tunnel syndrome due to their genetic makeup.
Age and Gender: Women and older individuals are more likely to develop carpal tunnel syndrome.
Certain Occupations: People who work in jobs that require repetitive motions of the hand and wrist, such as data entry or meatpacking, are at a higher risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome.
Certain Hobbies: Certain hobbies that require repetitive hand and wrist movements, such as knitting and gardening, may increase the risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome.

Treatments for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Treatment for carpal tunnel syndrome depends on the severity of the condition and may include rest, wrist splinting, medications, physical therapy, surgery, or alternative therapies.
Here are some common treatments:
Rest: Resting the affected hand and wrist and avoiding activities that aggravate symptoms can help reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms.
Wrist Splinting: Wearing a wrist splint can help keep the wrist in a neutral position, reducing pressure on the median nerve and alleviating symptoms.
Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain. In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be recommended to reduce inflammation.
Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can teach exercises to help strengthen the hand and wrist and improve flexibility.
Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be recommended to relieve pressure on the median nerve. During the surgery, the transverse carpal ligament is cut to relieve pressure on the nerve.
Alternative Therapies: Some people find relief from carpal tunnel syndrome symptoms through acupuncture, yoga, or chiropractic adjustments.
Frequently Asked Questions
Symptoms typically include numbness, tingling, and pain in the hand and fingers, especially during activities involving wrist flexion or extension.
Diagnosis is usually made through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests such as nerve conduction studies or electromyography.
Surgery is generally considered when conservative treatments fail to provide relief, or if symptoms are severe and affecting daily activities.
Recovery varies depending on the procedure but typically involves a period of rest, use of a splint, and gradual return to normal activities. Physical therapy may be recommended to aid in rehabilitation.
Most patients experience significant relief of symptoms and improved hand function after treatment. Long-term effects are rare, but maintaining proper wrist ergonomics and avoiding repetitive stress can help prevent recurrence.
Request an appointment
Please complete the details and we will book you shortly.
Request an appointment
Please complete the details and we will book you shortly.
